English
Insulated Copper Tube
Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-08 Origin: Site








You should pick insulation for copper pipe insulated by checking pipe size, insulation thickness, if the material works together, and if the pipe carries hot or cold water. In 2025, people often choose from these types:
Polyurethane and polyisocyanurate foam
Cellular glass
Fiberglass
Elastomeric foam
When you insulate copper pipe insulated, you help save energy. Studies say buildings with good insulation can save 10 to 45 percent on energy.
Building Type | Energy Savings Impact |
|---|---|
Residential Buildings | 10 to 45 percent energy savings with proper insulation |
Commercial Buildings | Over 700 therms of natural gas saved each year with insulation upgrades in 25% of old space |
Do not make mistakes like choosing the wrong size or material. Use new ways to get better results.
Pick the best insulation material for what you need. Foam, rubber, and fiberglass work in different ways and places.
Good insulation helps save energy and lowers your bills. Insulated pipes can cut energy costs by 10 to 45 percent. This makes your home use less energy.
Measure your copper pipes carefully before you buy insulation. The right size stops gaps and makes the insulation fit well. This helps it work better.
Choose insulation thickness by looking at your weather and pipe type. Thick insulation is needed in cold places to stop freezing. It also helps in wet places to stop water drops.
Seal every joint and seam when you put in insulation. Sealing right stops heat from escaping and keeps out water. This makes your insulation work well.
Insulation on copper pipes helps save energy at home. It keeps heat inside the pipes. Your water stays warm for a longer time. You do not need to run water as much. This helps you reach the right temperature faster. Your heating system does not work as hard. You pay less for your utility bills.
Here is how pipe insulation changes your system:
Benefit | Insulated Pipes | Uninsulated Pipes |
|---|---|---|
Heat Loss | Less heat escapes | More heat escapes |
Water Temperature Increase | Water gets 2°F–4°F hotter | Water stays cooler |
Water Heater Setting | You can set it lower | You need it higher |
Waiting Time for Hot Water | You wait less | You wait more |
Energy Savings | You save more energy | You save less energy |
Insulation helps the environment too. Using less energy lowers your carbon footprint. It makes your home more sustainable.
Copper pipes move water in many homes. You need insulation to keep pipes safe in cold weather. Copper does not keep heat well. Pipes can freeze if left open to cold air.
In cold places, insulation keeps pipes above freezing. This stops damage. It is important for pipes in basements or attics.
Insulation protects pipes from freezing. You avoid expensive repairs and water damage.
Insulation stops water drops from forming on copper pipes. In humid places, warm air hits cold pipes. This makes water droplets. Moisture can cause mold and damage. Insulation blocks warm air from touching pipes. Pipes stay dry. Materials that resist moisture trap air. They keep the temperature steady. Condensation does not form.
Good insulation helps pipes last longer. It keeps pipes dry and stops water damage. It also prevents corrosion. Your HVAC system works better and saves energy.
Here are ways insulation helps with maintenance:
Stops condensation and water damage.
Keeps refrigerant temperature steady for HVAC.
Cuts energy loss and lowers bills.
Makes pipes and systems last longer.
Keeps air clean by stopping mold.
Helps your system work well all year.
Meets safety rules in building codes.
Insulation gives you peace of mind. It helps your home run smoothly.
There are many ways to insulate copper pipes. Each material works best for certain jobs. Here is a simple comparison:
Material | Temperature Suitability | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
Foam | Cold and hot pipes | Flexible, good for condensation control |
Rubber | Cold and hot pipes | Moisture resistant, durable, easy installation |
Fiberglass | High-temperature pipes | Excellent thermal resistance, minimizes energy loss |
Mineral Wool | High-temperature pipes | Fire-resistant, water-repellent, noise reduction |
Advanced Materials | Varies | Designed for specific applications |
Foam is used a lot for copper pipes. It works for hot and cold water lines. Foam helps stop water drops and saves energy. Polyethylene foam is popular because it bends easily. You can put it on pipes without trouble. It fits tight and keeps pipes dry.
Tip: Closed-cell foam stops moisture better than open-cell foam.
Foam insulation does not cost much and keeps heat well. If you do not put it on right, water can get in and cause mold.
Rubber insulation is good for wet places. It does not let mildew grow. Rubber can handle sunlight and chemicals. You can use it for hot or cold pipes. The closed cells keep heat inside and save energy. Rubber bends easily, so you can wrap it around corners.
Rubber insulation lasts long and needs little care.
It works in HVAC systems and places with changing heat.
Fiberglass is great for pipes that get very hot. You see it on hot water pipes and in big buildings. Fiberglass can take heat up to 1000°F. It keeps heat in and cuts energy loss. The glass strands help your system work better.
Fiberglass does not stop fire as well as mineral wool.
It is best where you need strong heat control.
Mineral wool is special because it does not burn. It keeps water out and lowers noise. You use it for copper pipes in hot places. Mineral wool helps stop fire from spreading. It also keeps pipes safe from water.
Mineral wool is good for buildings with tough fire rules.
It works in factories and homes.
New insulation types came out in 2025. Some use special mixes and are better for the planet. Advanced materials work well and last long. Some use recycled stuff to help nature. You might see aerogel or new rubber in buildings. These materials meet strict energy rules and last longer.
Note: Advanced insulation costs more, but saves energy and needs less fixing later.
When you pick insulation for copper pipes, think about heat, wetness, and fire safety. The right choice protects pipes and saves energy.
You need to measure pipes before buying copper pipe insulation. First, check the length from one end to the other. Use a caliper to measure across if the pipe is round. If the pipe is oval, measure both sides and find the average. Most copper pipes have their internal diameter stamped on them. But you should always measure the outside diameter for the right size. Use millimeters to match insulation products more easily. Repeat these steps for every part, especially if pipes bend or curve.
Steps for measuring copper pipe diameter:
Measure the whole length of each pipe.
Use a caliper to find the diameter. For oval pipes, measure both sides and average.
Look for diameter stamps, but always check with your own measurement.
Write down measurements for every part, including bends.
Tip: Measuring carefully helps you avoid gaps and makes sure you pick the right size insulation for your copper pipes.
Insulation thickness changes how well copper pipe insulation works. Thicker insulation keeps heat inside hot water pipes. It also blocks cold from getting in. If you live in a cold place, you need thicker insulation to stop pipes from freezing. In humid places, thicker insulation helps stop condensation. Always check local building codes because they may set the smallest insulation thickness.
Factors that affect insulation thickness:
Pipe size: Bigger pipes need thicker insulation.
Temperature: Hot water pipes need more insulation to keep heat in. Cold water pipes need enough to stop condensation.
Climate: Colder places need thicker insulation for freeze protection.
Building codes: Rules may require a certain thickness.
Material: Some insulation materials work better than others.
Manufacturer guidelines: Always check what the maker says.
Note: Picking the right size insulation helps you save energy and keeps pipes safe.
When you look for copper pipe insulation, check the R-value. The R-value shows how well insulation stops heat from moving. Higher R-values mean better efficiency. In homes, you want insulation with a good R-value to keep energy costs low. In commercial buildings, higher R-values help systems work better and save more energy. The right size pipe insulation with a high R-value gives you the best efficiency.
R-value matters for both hot and cold pipes.
Flexible and lightweight insulation works well for pipes that change temperature.
Always match the R-value to your needs for maximum efficiency.
You must pick insulation that matches your copper pipes. Some materials work better with copper. Foam and rubber insulation fit most copper pipes and help control condensation. Fiberglass and mineral wool work well for high-temperature pipes. Advanced materials like aerogel offer extra efficiency and last longer. Make sure your insulation does not react with copper or cause corrosion.
Tip: Picking the right size insulation and the right material keeps pipes safe and helps your system run smoothly.
Hot and cold pipes need different copper pipe insulation. Hot water pipes lose heat fast, so you need thicker insulation. Cold water pipes need insulation to stop condensation. Use the right size pipe insulation for each type.
Pipe Type | Recommended Insulation Thickness |
|---|---|
Hot Water | 1" for pipes up to 2" IPS, 1-1/2" for larger pipes |
Cold Water | 1/2" to prevent condensation |
Hot water pipes: Use thicker insulation for better efficiency.
Cold water pipes: Use enough insulation to keep pipes dry.
Where you put copper pipe insulation matters. Indoor pipes in humid or air-conditioned spaces need foam or rubber insulation to stop condensation and mold. Outdoor pipes need weather-resistant insulation, like rubber foam, to handle sun and rain. Pipes in attics or unheated spaces need thicker insulation for freeze protection.
Installation Environment | Recommended Insulation Type | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
Indoor (humid/air-conditioned) | Foam or rubber insulation | Stops condensation and mold growth |
Outdoor | Weather-resistant materials (e.g., rubber foam) | Handles sun and temperature changes |
Unconditioned spaces (e.g., attics) | Thicker insulation (1-inch) | Better protection against freezing |
Colder regions | Thicker insulation | Needed for stopping freezing |
Warmer climates | Focus on condensation control | Reduces moisture problems |
Remember: Picking the right size insulation and the correct type for your space helps you meet building codes and keeps pipes working well.
Summary for copper pipe insulation selection:
Measure pipes carefully.
Pick the right size pipe insulation for a snug fit.
Choose insulation thickness based on pipe type and climate.
Check R-value for best efficiency.
Match insulation material to your copper pipes.
Use the right insulation for hot or cold pipes.
Pick weather-resistant insulation for outdoor pipes.
Always follow local codes and manufacturer guidelines.
Get your workspace ready before you start. Gather your insulated copper pipe kit. Check if all the parts are there. Good kits have copper pipes, insulation, and fittings. You can pick insulation thickness and wall thickness. These choices help you match your project.
Component | Description |
|---|---|
Pipe Size | Pick the right size for good flow and efficiency. |
Insulation Material | Elastomeric or nitrile foam rubber keeps heat in and temperatures steady. |
Insulation Thickness | Choices go from 3/8” to 1” for different needs. |
Pipe Strength | Pure copper pipes last longer and resist damage. |
Wall Thickness | Pick from 0.6mm to 3mm for your job. |
Ease of Installation | Pre-insulated kits make work faster and easier. |
Cost Considerations | Good kits save money and help energy efficiency. |
Look at the copper pipes before you begin. Make sure they are clean and dry. Take off any dirt, oil, or old insulation. This helps new insulation stick and last longer.
Follow these steps to get pipes ready:
Ream the cut end to remove burrs.
Deburr or chamfer the outside to protect gaskets.
Straighten and re-round ends for a tight fit.
Tip: Careful prep helps you install right and stops leaks or gaps.
Cut the copper pipe and insulation to the right length. Use a pipe cutter for straight cuts. In small spaces, use a hacksaw. Always measure two times before you cut.
Fit the insulation so it covers the pipe fully. It should fit tight with no gaps. For bends or corners, use preformed pieces or cut insulation to fit. Nitrile foam rubber bends easily for tight spots.
You need these tools for cutting and fitting:
Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
TIK-C585 Pipe Caliper | Measures pipe size for picking insulation. |
Carborundum Sharpening Stone | Keeps tools sharp for smooth cuts. |
Rubber/PVC Glue Guns | Puts glue on insulation evenly. |
Pipe Cutters | Makes clean cuts on copper pipes. |
Hacksaw | Cuts pipes or insulation in hard places. |
Guides say sharp tools stop rough edges that hurt insulation or pipes.
Seal all joints and seams to keep heat in and water out. Use preformed insulation for elbows, tees, and valves. If you do not have these, cut pieces from straight insulation and fit them around joints.
Put insulation tape or glue on all seams for extra protection. This makes a strong barrier and keeps your system working well. You can use insulating cements for a tight seal.
Seal joints or ends where insulation meets.
Use more tape or glue for a strong, water-proof seal.
Check all fittings and valves for gaps.
Note: Sealing well is a big benefit of insulating copper pipes. It keeps your system safe and saves energy.
You need the right tools for easy installation. The kit may have some tools, but you might need more for best results.
Pipe Cutters: For straight cuts on copper pipes.
Hacksaw: For cutting in tight spaces.
Carborundum Sharpening Stone: Keeps tools sharp.
Rubber/PVC Glue Guns: For putting glue on insulation.
TIK-C585 Pipe Caliper: Measures pipe size for a good fit.
Using the right tools makes installation easier and helps you avoid mistakes.
Safety is important for every installation. Always wear safety glasses, gloves, and a hard hat. Handle insulation carefully to avoid cuts or skin problems. If you work high up, use harnesses and lanyards.
Check your work area for dangers before you start. Look at ladders and scaffolding to make sure they are safe. Know where emergency exits are and learn first aid steps.
Wear safety gear all the time.
Handle insulation and pipes with care.
Use fall protection when needed.
Check your tools and workspace before starting.
Learn emergency steps.
Safety first: These steps protect you and help the job go smoothly.
People make mistakes during installation. Here are some common problems and how to avoid them:
Picking the wrong size insulation: Measure pipes carefully and use a pipe caliper.
Leaving gaps or loose joints: Fit insulation tight and seal all seams.
Using the wrong material: Match insulation to your pipe and space. Spray foam and mineral wool work with copper pipes, but check if they fit.
Skipping prep: Clean and deburr pipes before you put on insulation.
Ignoring safety: Always wear safety gear and check your workspace.
Guides say good installation stops leaks, saves energy, and makes your system last longer.
Follow this guide for the best results. Using pre-insulated copper pipe kits makes the job easier and faster. When you use the right kit, you get better performance and fewer repairs. Insulating copper pipes gives you lower bills, longer pipe life, and a safer home.
Picking the wrong insulation size is a common mistake. If insulation is too small, it will not fit. If it is too big, it leaves gaps. Gaps make your pipes lose energy. Always measure the outside of your copper pipe before buying insulation. Use a pipe caliper for the best measurement. The chart below shows which insulation size fits each pipe diameter:
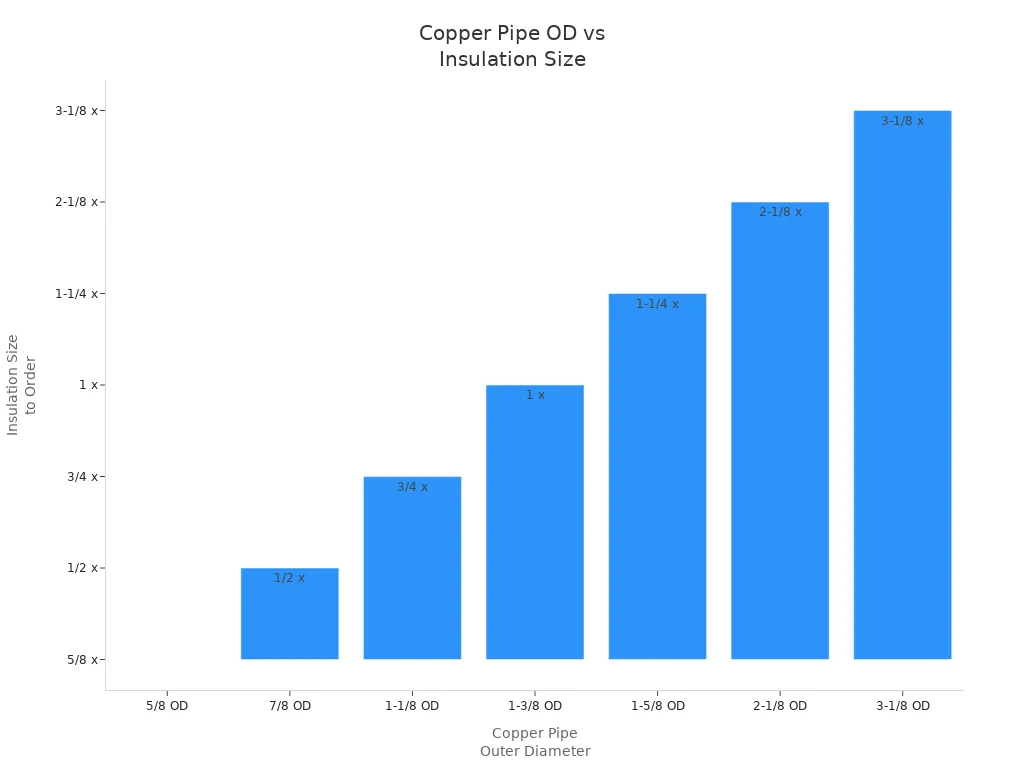
If insulation feels loose or tight after you put it on, check your measurements. Replace the insulation with the right size.
Using the wrong insulation material causes problems. Foam and rubber insulation work best for most copper pipes. If you use the wrong material, you might see water drops or lose heat. Always pick insulation made for copper pipes and your job. For air conditioning pipes, use rubber or foam to stop water drops. For hot pipes, fiberglass or mineral wool works better.
Gaps or missing insulation make it work less well. Air can leak through gaps and raise your bills. If you squeeze insulation too much, it does not work as well. Make sure you cover pipes fully, especially at joints and valves. The table below lists common mistakes and how to fix them:
Mistake | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
Leaving Gaps and Incomplete Coverage | Gaps let air leak and make insulation weaker. | Put insulation on with no empty spots, especially near outlets and plumbing. |
Compressing Insulation | Squeezing insulation too much makes it less effective. | Follow the instructions so insulation stays fluffy. |
Poor Vapor Barrier Installation | Bad vapor barriers let in water and cause damage. | Seal vapor barriers at seams and edges to keep water out. |
Neglecting Air Sealing | Air leaks make insulation work worse. | Seal cracks or gaps before you put on insulation. |
Using the Wrong R-Value | Picking the wrong R-value wastes energy. | Use the right thickness and type for your climate and local rules. |
Failing to Stay Updated on Best Practices | Not learning new ways can make insulation work poorly. | Keep learning about new materials and methods to do better. |
Think about where you put insulation. Outdoor pipes need insulation that can handle weather. In wet places, use insulation that blocks water. If you ignore these things, insulation can break or let water in. Always match insulation to your climate and location.
If you find broken or badly installed insulation, do this:
Look at the insulation and pipe for damage or leaks.
Turn off the water before you fix anything.
Take off damaged insulation and clean the pipe.
Measure and cut new insulation to fit.
Put on the new insulation so it fits tight.
Seal all joints and seams with tape or glue.
Turn the water back on and check for leaks.
Check your work to make sure there are no gaps.
Tip: Check your insulation often and fix problems fast. This helps your insulation last longer and keeps your pipes safe.
You can put insulation on copper pipes by measuring the pipe size. Pick a material that works well. Make sure the insulation fits tightly. Good insulation helps you in many ways:
You use less energy and pay lower bills.
You stop water leaks and keep your pipes safe.
You make your system work better.
Learn about new insulation rules and standards. NAIMA and other experts have helpful guides. If you are not sure, ask a licensed expert for help.
Pick insulation based on your weather and how you use pipes. Foam and rubber are good for most homes. Thicker insulation keeps heat in and protects pipes in cold places.
Insulation on copper pipes helps your hvac work better. It stops heat from escaping. Your system uses less energy to keep water hot or cold. This means you save money on bills.
Good insulation protects pipes and lasts longer. High-quality products stop leaks and damage. You get fewer repairs and more reliable pipes.
Yes. Energy efficient insulation helps your hvac last longer. It keeps pipes dry and safe. This lowers the chance of breakdowns and makes your system work well.
Look for insulation that fits tight with no gaps. Strong seams keep pipes dry. Check your insulation every year to make sure it still works.




